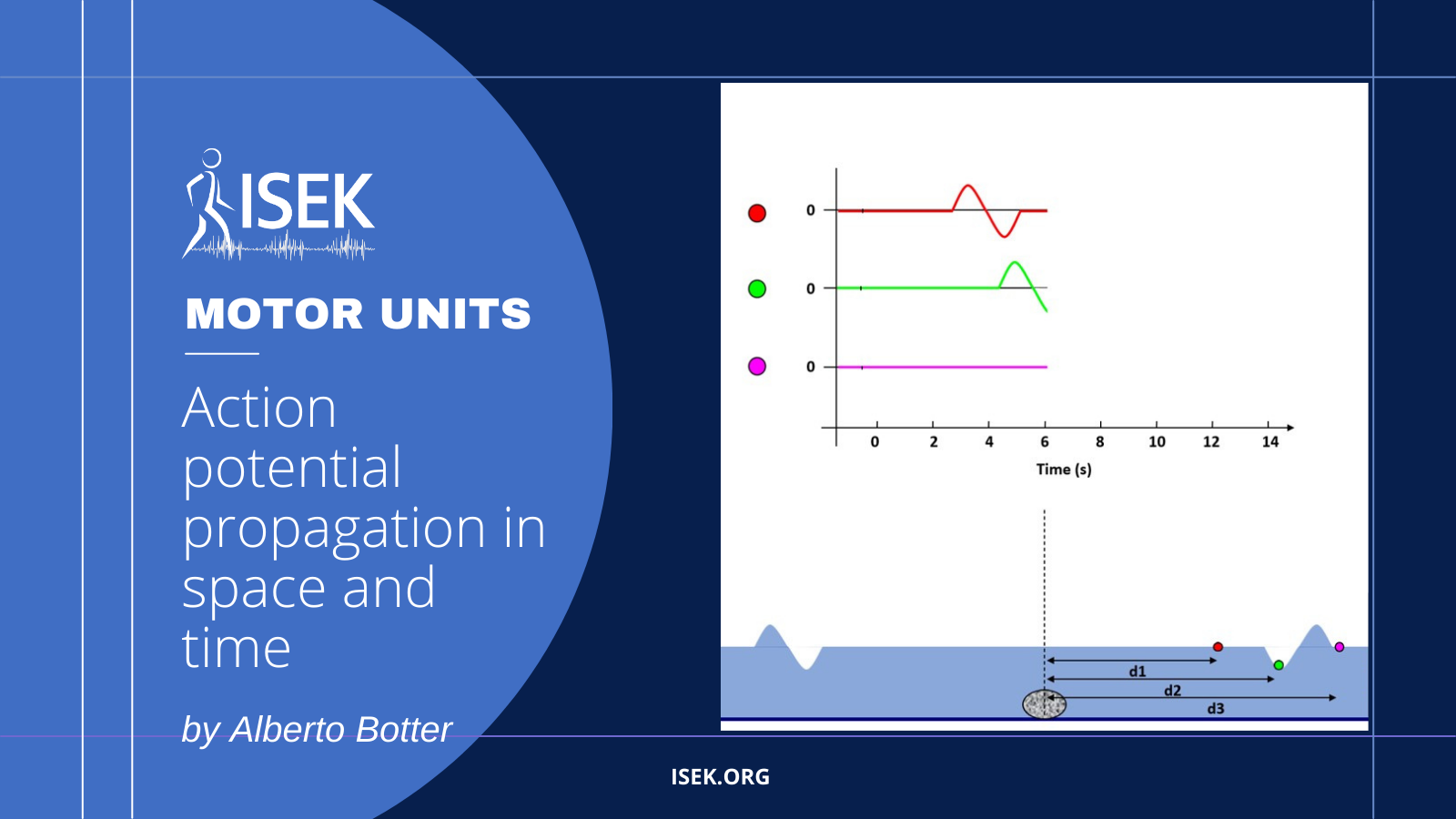
Understanding how action potential propagation in muscle fibres can be assessed from surface EMG
This material was prepared with the goal of illustrating how surface EMGs convey information on the propagation of action potentials. Analogy is made to the wave generated by dropping a rock on a water tank. The propagation of the water wave generated when the rock hits the water surface can be assessed by measuring the height of multiple floating objects positioned serially along the water. Similarly, the propagation of action potentials generated at the end plates can be assessed by measuring the surface, electric potential with electrodes positioned consecutively along the skin.
About the Author

Alberto Botter
Laboratory for Engineering of the Neuromuscular System, Politecnico di Torino, Italy
Ph.D. in Biomedical Engineering (2011). He is currently Associate Professor in Biomedical Engineering at Politecnico di Torino. His research interests include neuromuscular electrical stimulation, surface EMG, electrode technology, and signal processing applied to biomedical signals.