Identification of propagating action potentials with bidimensional grids of surface electrodes
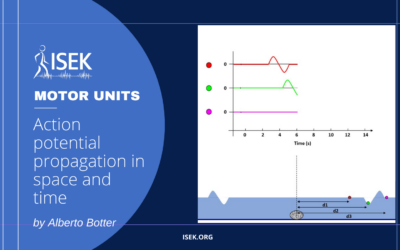
The muscle fibre conduction velocity (CV) is the speed with which action potentials travel along the muscle fibres. Owing to its sensitivity to events of applied interest (e.g. muscle fatigue), CV earns relevance for the study of the neuromuscular system. The popularity of CV assessment increased after arrays of surface electrodes have been developed: CV can be estimated non-invasively.
Even though a linear array of electrodes is sufficient for providing CV estimates, its representativeness and accuracy may be an issue. This material illustrates why a bidimensional grid of electrodes is preferred over linear arrays for CV estimation. In slides 1 and 2 the user is invited to identify how many sources (in this example different cars represent different action potentials) are travelling. With a linear array only one source is visible while different sources are revealed with a 2D mapping: representativeness increases. In slide 3 the source travels not parallel to rows and columns of detection points, biasing any attempt to estimate CV from either rows or columns alone. Only when considering detection points crossing rows and columns the direction of the travelling source can be identified: accuracy increases.
About the Authors

Corrado Cescon
University of Applied Science of Southerns Switzerland
Corrado Cescon is a senior researcher at the Rehabilitation Research Laboratory (2rLab) of the University of Applied Science of Southerns Switzerland (SUPSI). His research interests are EMG signal processing, image processing and motion capture analysis.

Taian Vieira
Politecnico di Torino
Taian Vieira is with the Laboratory for Engineering of the Neuromuscular System (LISiN), Politecnico di Torino, Italy. His research activities focus on the extraction of information of valid, applied interest from surface electromyograms.